In today’s digitally connected, regulation-heavy, and risk-conscious environment, businesses of all sizes face increasing pressure to protect information, demonstrate compliance, and build stakeholder trust. ISO certification, particularly ISO/IEC 27001:2022 for information security management, provides a globally recognised framework to achieve all three.
Whether you are a small startup scaling up or a multinational corporation managing complex operations across multiple geographies, ISO certification is more than a badge, it is a strategic investment.
What Is ISO Certification?
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) certifications validate that an organisation operates in accordance with international standards across multiple areas, including:
- Information Security (ISO/IEC 27001:2022)
- Quality Management (ISO 9001:2015)
- Environmental Management (ISO 14001:2015)
- Privacy Information Management (ISO/IEC 27701:2019)
- Risk Management (ISO 31000:2018)
The ISO/IEC 27001:2022 standard specifically outlines requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
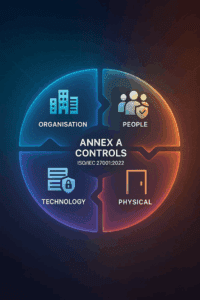
It is supported by 93 updated security controls, listed in Annex A, categorised into four key themes:
- Organisational
- People
- Physical
- Technological
Benefits of ISO Certification for Small Companies
Small organisations often believe ISO certification is only for large enterprises. In reality, achieving ISO/IEC 27001:2022 or ISO 9001:2015 early on sets the foundation for growth, credibility, and compliance.
- Build Trust and Market Credibility
For small companies, especially those in tech, consulting, or SaaS, ISO/IEC 27001:2022 instantly boosts credibility with enterprise clients.
Example: A 12-person cybersecurity startup in Cape Town secured a government health contract after achieving ISO/IEC 27001:2022. This eliminated the need to complete a 50-page internal security assessment.
- Clause 4.2: Understanding the needs of interested parties
- Control A.5.36: Demonstrates conformance with rules and policies
- Gain Competitive Advantage in Procurement
Large corporations, governments, and financial institutions increasingly mandate ISO certification as a prerequisite for suppliers.
Example: A digital marketing agency in Pretoria reported a 40% higher tender success rate within six months of achieving ISO/IEC 27001:2022 certification. This helped remove procurement barriers, improve RFP success, and accelerate onboarding.
- Establish Operational Maturity Early
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 forces small businesses to move away from informal structures by formalising policies, processes, and responsibilities.
- Control A.5.2: Assigns clear information security responsibilities
- Clause 5.3: Organisational roles and responsibilities
Example: A startup that heavily relied on freelancers implemented a formal access control and offboarding process using A.5.18 (Access rights), reducing the risk of data leakage.
- Demonstrate Legal Compliance Easily
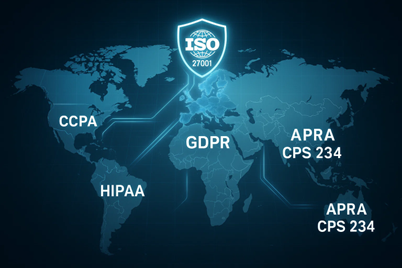
Many small businesses are unaware of the legal implications of mishandling personal data. ISO/IEC 27001:2022 provides a structured framework for compliance with data protection laws, such as the EU GDPR, Australia’s Privacy Act, and California’s CCPA.
- Control A.5.31: Legal, regulatory, and contractual requirements
- Control A.5.34: Privacy and protection of PII
Example: A healthcare startup in Sydney leveraged ISO/IEC 27001:2022 to align its compliance roadmap with the Privacy Act 1988 and the Notifiable Data Breach Scheme.
- Prepare for Investment or Acquisition
ISO certification signals governance maturity, an increasingly critical factor for investors conducting due diligence.
Example: A fintech startup raised R6M Series A funding, with investors citing the company’s certified ISMS and independent audit as proof of robust risk management.

Benefits of ISO Certification for Large Companies
Large organisations face different challenges compared to small companies, managing complexity, standardising practices, and ensuring compliance across multiple jurisdictions. ISO certification provides a strategic mechanism for governance, resilience, and trust.
- Standardisation Across Global Operations
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 creates a unified structure across international operations.
Example: A multinational logistics provider harmonised 18 regional security policies into one ISO framework, using Clause 4.3 (Scope) and A.5.1 (Policies for Information Security).
- Robust Legal and Regulatory Defensibility
With overlapping regulations across different regions, ISO/IEC 27001:2022 ensures consistent compliance.
- Control A.5.31: Regulatory and contractual alignment
- Clause 6.1.3: Risk treatment aligned with legal risk
Example: A global cloud services company relied on ISO/IEC 27001:2022 during a cross-border investigation to prove compliance with 14 separate data protection laws.
- Supply Chain Risk Management
Third-party risks are among the biggest vulnerabilities for large organisations. ISO/IEC 27001:2022 strengthens supplier due diligence.
- Controls A.5.19–A.5.22: Supplier lifecycle management
Example: A bank mandated ISO/IEC 27001:2022 certification for 65 critical vendors following a major supply chain data breach.
- Business Continuity and Resilience
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 requires resilience planning, particularly in the face of cyberattacks and operational disruptions.
- Control A.5.29: Information security during disruption
- Control A.5.30: ICT readiness for business continuity
Example: A retail group maintained uninterrupted operations during a ransomware attack by activating ISO-driven continuity plans.
- Strategic Governance and Oversight
Boards and executives demand visibility of cyber risks. ISO/IEC 27001:2022 embeds performance evaluation and continuous improvement into governance.
- Clause 9.3: Management review
- Clause 10.1–10.2: Corrective actions and continual improvement
Example: An enterprise media company built real-time dashboards (Clause 9.1 metrics) to track ISMS performance and report cyber risk at board level.
- Sustainable Practices and Climate Accountability
As of 2024, ISO management system standards require organisations to consider climate change when determining external issues and interested party needs.
- Clause 4.1: External issues must now consider climate change
- Clause 4.2: Interested parties may have climate-related requirements
Example: An energy infrastructure company integrated ISO/IEC 27001:2022 with ISO 14001:2015 to manage both cybersecurity and environmental risk in its governance framework.

Final Thoughts
ISO certification, whether for information security, quality control, environmental management, or risk management, is more than a compliance exercise. For small companies, it unlocks market entry, trust, and investment opportunities. For large corporations, it ensures resilience, governance, and global consistency.
By adopting standards such as ISO/IEC 27001:2022, organisations can demonstrate operational maturity, meet legal obligations, and build sustainable practices that protect both stakeholders and long-term growth.
Whether you are a startup looking to win enterprise clients or a large corporation seeking consistency across global operations, our experts can help you achieve certification.
WWISE provides:
- Gap assessments and risk assessments
- ISO/IEC 27001:2022 consulting and implementation
- End-to-end certification support
Partner with WWISE today to unlock the true value of ISO certification for your organisation.

